Introduction
Welcome, bird enthusiasts and curious minds! Today, we are going to explore the fascinating world of the Canada Goose. These birds are among the most recognizable and widespread waterfowl in North America. Whether you’re strolling through a city park, hiking near a lake, or driving by open fields, chances are you’ve encountered these majestic birds. But there’s much more to the Canada Goose than meets the eye.
In this journey, we’ll delve into various aspects of the Canada Goose’s life, from their striking appearance and unique nesting habits to their favorite foods and some fun, lesser-known facts. We’ll also touch on the important conservation efforts that help protect these birds and ensure their populations remain healthy.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the Canada Goose and its role in our natural world. So, grab your binoculars and join me as we uncover the wonders of the Canada Goose.
Appearance

The Canada Goose is a sight to behold, with its elegant posture and distinctive markings. Let’s take a closer look at the key features that make this bird so recognizable.
Size and Shape
The Canada Goose is a large bird, often reaching lengths of 30 to 43 inches, with a wingspan that can stretch up to 6 feet. They are characterized by their long necks and sizable bodies, which give them a graceful yet imposing presence, whether on the ground or in the air.
Distinctive Markings
One of the most iconic features of the Canada Goose is its black head and neck, contrasted by a striking white “chinstrap” that stretches from ear to ear beneath its beak. This white marking is a primary identification feature and sets the Canada Goose apart from other similar species.
Plumage
The body of the Canada Goose is covered in a mix of brown and gray feathers, which help it blend seamlessly into its natural surroundings, like wetlands and grasslands. The back and upper wings are typically darker, while the chest and sides are lighter, sometimes appearing almost white. This variation in color provides excellent camouflage against predators.
Beak and Legs

Their beak and legs are both black, complementing the black of their head and neck. The beak is strong and slightly hooked at the tip, perfect for grazing on grasses and other vegetation. Their webbed feet are well-suited for swimming, allowing them to navigate water with ease.
Variations and Subspecies
There are several subspecies of Canada Goose, varying slightly in size and coloration. The “giant” subspecies, found primarily in the Midwest, is the largest, while the “lesser” Canada Goose, which breeds in the Arctic, is noticeably smaller. Despite these variations, the core characteristics remain consistent across all subspecies.
Molting and Seasonal Changes
Canada Geese undergo a molting process each year, during which they lose and regrow their flight feathers. This molt occurs after the breeding season and can render them temporarily flightless. During this period, they seek out safe areas with abundant food and water. Their plumage can also change slightly with the seasons, appearing more vibrant in the spring and summer and more subdued in the fall and winter.
Juvenile Appearance
Young Canada Geese, known as goslings, have a different appearance compared to adults. They are covered in soft, yellowish down when they hatch, which gradually changes to grayish-brown as they mature. The characteristic black and white markings develop as they approach adulthood, around one year old.
Understanding the appearance of the Canada Goose is crucial for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts alike. These features not only help identify the birds but also give insights into their behavior and adaptations to their environment.
Nesting Habits

The nesting habits of the Canada Goose are as intriguing as their appearance. Let’s explore how these birds choose their nesting sites, build their nests, and care for their young.
Nesting Sites
Canada Geese are versatile when it comes to selecting nesting sites. They prefer areas near water bodies such as lakes, rivers, ponds, and marshes. Proximity to water is crucial as it provides a safe escape route from predators and a steady supply of food. However, these adaptable birds can also be found nesting in urban areas, including parks, golf courses, and even rooftops.
Nest Construction
The female Canada Goose takes the lead in nest building while the male stands guard. Nests are typically constructed on the ground in a slightly elevated area to prevent flooding. They often reuse the same nesting sites year after year, which can lead to significant wear on the surrounding vegetation.

The nest itself is a simple but effective structure. It is made from a variety of materials, including grasses, mosses, and twigs, lined with soft down feathers plucked from the female’s own body. This down not only provides insulation but also makes the nest cozy and comfortable for the eggs.
Egg Laying and Incubation
A typical clutch consists of 4 to 7 eggs, which are creamy white. The female Canada Goose incubates the eggs, a process that lasts about 25 to 30 days. During this period, the male remains close by, fiercely protecting the nest from potential threats. The female leaves the nest only briefly to feed, relying on the male to keep watch.
Hatching and Early Life
Once the eggs hatch, the goslings are remarkably well-developed. They are covered in down and have their eyes open, ready to leave the nest within 24 hours. This immediate mobility is crucial for their survival, as the family must quickly move to water to evade predators and find food.
Parental Care
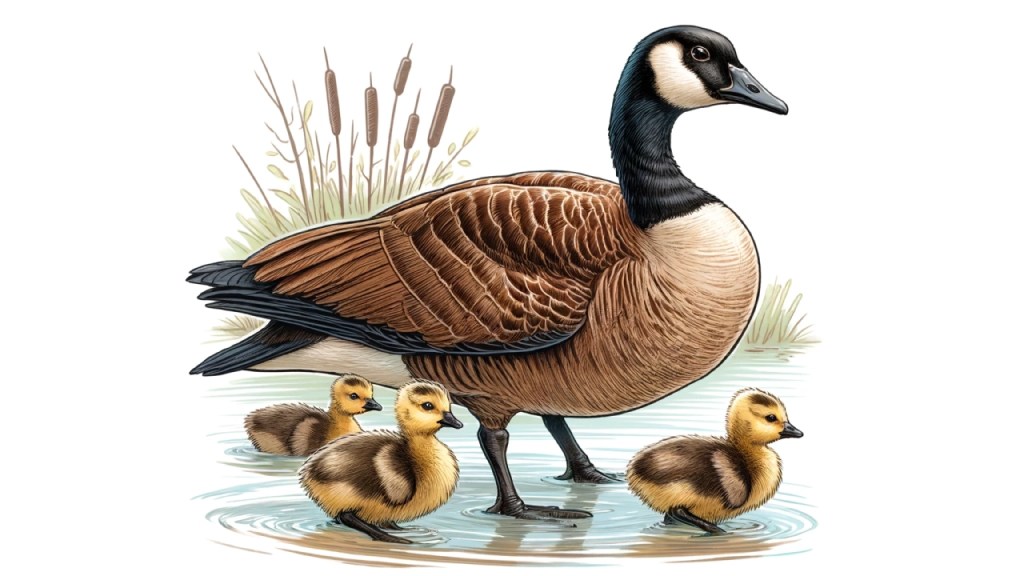

Both parents are highly involved in raising their young. The goslings stay with their parents for an extended period, often until they migrate in the fall. During this time, the parents teach them essential survival skills, such as foraging for food and recognizing danger. The strong family bonds help ensure that the goslings have the best possible start in life.
Migration Patterns
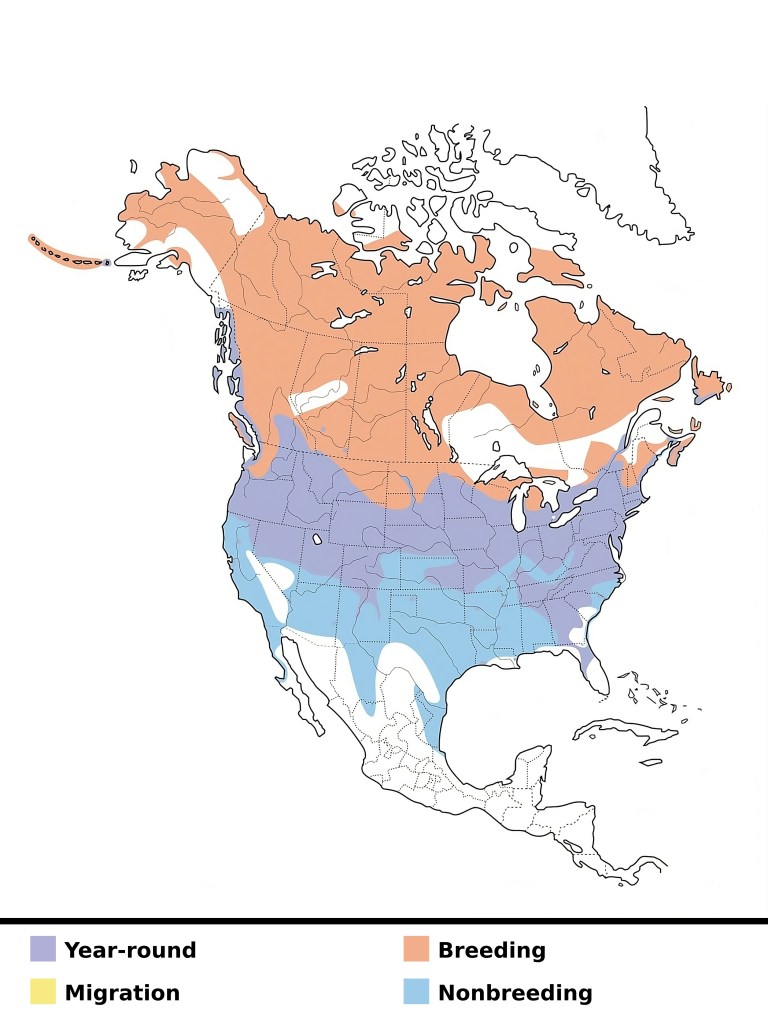
Canada Geese are known for their impressive migratory behavior. Families typically migrate together, traveling in the familiar V-formation that helps conserve energy. They cover vast distances between their breeding grounds in the north and their wintering grounds in the south. Migration routes are learned behaviors that are passed down from generation to generation.
Challenges and Adaptations
Nesting can be a risky endeavor for Canada Geese, as they face threats from predators such as raccoons, foxes, and birds of prey. Human activities and habitat destruction also pose significant challenges. Despite these threats, Canada Geese have shown remarkable resilience. Their ability to adapt to different environments and their strong parental instincts contribute to their success as a species.
Understanding the nesting habits of Canada Geese gives us a deeper appreciation for these birds’ dedication and adaptability. Their nesting strategies are evidence of their resilience and intelligence, allowing them to thrive in a variety of environments.
Favorite Foods
Canada Geese have a diverse diet that changes with the seasons and their habitats. Understanding their feeding habits provides insights into their adaptability and survival strategies.
Primary Diet
The Canada Goose is primarily herbivorous, feeding on a variety of plants. Their diet mainly consists of grasses, sedges, grains, and aquatic vegetation. This makes them well-suited to both natural wetlands and agricultural areas, where they can often be seen grazing.
Grazing and Foraging
On land, Canada Geese are avid grazers. They prefer lush, green grasses found in fields, parks, and golf courses. During the growing season, they feed extensively on young shoots and leaves. Their strong, serrated beaks are perfect for snipping off vegetation close to the ground.
In aquatic environments, Canada Geese forage for submerged vegetation. They dabble in the water, using their beaks to pull up roots, tubers, and stems of plants like pondweed and eelgrass. This ability to exploit both terrestrial and aquatic food sources is key to their widespread success.
Seasonal Diet Changes

The diet of the Canada Goose varies with the seasons. During the spring and summer, when vegetation is abundant, they consume large quantities of grasses and other green plants. As the seasons change and plants become less available, their diet shifts.
In the fall, Canada Geese take advantage of agricultural leftovers. They often feed in harvested fields, eating spilled grains like corn, wheat, and barley. This not only provides a rich food source but also helps farmers by cleaning up grain waste.
During the winter, when natural food sources are scarce, Canada Geese rely more on grains and seeds. In some urban areas, they may also consume human-provided food, although this is less common.
Feeding Behavior
Canada Geese exhibit several interesting feeding behaviors. They often feed in groups, which provides safety in numbers and helps locate food more efficiently. When feeding in fields, one or more geese usually keep watch for predators while the rest of the group grazes.
In water, their feeding is characterized by “upending,” where they tip forward to reach underwater plants. This behavior is common in shallow ponds and lakes, allowing them to access food that other birds might miss.
Nutritional Needs

The diverse diet of Canada Geese meets their nutritional needs throughout the year. Fresh greens provide essential vitamins and minerals, while grains and seeds offer carbohydrates for energy. Their diet’s adaptability allows them to thrive in various environments and during different seasons.
Human Interaction
In many areas, Canada Geese have adapted to living near humans. Urban parks and golf courses often provide abundant food and safe nesting sites. However, feeding geese human food, such as bread, is discouraged as it can lead to poor nutrition and dependency. If you want to feed them, it’s best to give them uncooked rolled oats or cracked corn.
Environmental Impact
The feeding habits of Canada Geese can have significant impacts on their environment. While grazing, they can help control the growth of certain plant species, maintaining healthy ecosystems. However, in large numbers, they can also cause damage to crops and overgraze fields. Managing their populations and habitats is crucial to balancing these impacts.
Understanding the favorite foods and feeding behaviors of Canada Geese highlights their adaptability and the intricate balance they maintain with their environment. Their ability to find food in various settings is a testament to their resilience and resourcefulness.
Fun Facts
Canada Geese are full of surprises and interesting traits that make them even more fascinating. Let’s explore some fun facts about these remarkable birds.
Impressive Navigators
Canada Geese are known for their incredible migratory journeys, often traveling thousands of miles between their breeding and wintering grounds. They navigate using a combination of innate instinct and learned behaviors. Remarkably, they can recognize landmarks and use the position of the sun and stars to find their way.
V-Formation Flight
One of the most iconic sights in nature is the V-formation of flying geese. This formation is not just visually striking; it serves a practical purpose. By flying in a V, geese reduce wind resistance and conserve energy. The lead bird breaks the wind, creating an updraft for the birds behind it. They take turns leading, allowing each bird to rest while benefiting from the formation.
Strong Family Bonds
Canada Geese are known for their strong family bonds. Mated pairs often stay together for life, and both parents share responsibilities in raising their young. Goslings remain with their parents for several months, learning vital survival skills. These close-knit family groups are often seen migrating together.
Remarkable Adaptability

These birds are incredibly adaptable and can thrive in a wide range of environments, from remote wilderness areas to bustling urban parks. Their ability to find food and nesting sites in various settings has contributed to their widespread presence across North America.
Communication Skills
Canada Geese are highly vocal birds, using a range of calls to communicate. Their familiar honking serves multiple purposes, from maintaining group cohesion during flight to warning of potential dangers. Each goose has a unique voice, allowing them to recognize each other’s calls, even in large flocks.
Longevity and Lifespan
In the wild, Canada Geese can live up to 20 years, though the average lifespan is typically around 10 to 15 years. Their strong social structures and adaptability aid their longevity. In captivity, some geese have been known to live even longer, reaching up to 30 years.
Altruistic Behavior
Canada Geese exhibit altruistic behavior, particularly during migration. When a goose is sick or injured, a few others from the flock will stay behind to provide support and protection until the bird is able to continue or passes away. This selfless behavior underscores the strong social bonds within their groups.
Unique Molting Process

Each year, Canada Geese undergo a molting process, during which they lose and regrow their flight feathers. This usually occurs after the breeding season and renders them temporarily flightless. During this vulnerable time, they seek out safe areas with abundant food and water to avoid predators.
Iconic Symbol
The Canada Goose is an iconic symbol of North America and is often featured in art, literature, and folklore. Its migratory patterns and majestic presence have inspired countless stories and representations, highlighting its significance in both natural and cultural contexts.
Environmental Indicators
Canada Geese can serve as an indicator of environmental health. Changes in their population sizes and migratory patterns can signal shifts in ecosystems and climate conditions. Monitoring these birds helps scientists understand broader ecological trends and the impacts of human activity on wildlife.
Cultural Impact
Canada Geese have made their mark on human culture, featuring in various cultural references and even sports team mascots. Their presence is a reminder of the interconnectedness of nature and human society.
These fun facts about Canada Geese offer a glimpse into the unique characteristics and behaviors that make these birds so captivating. Their adaptability, social structures, and the roles they play in ecosystems highlight their importance in the natural world.
Conservation Efforts

The story of the Canada Goose is one of remarkable recovery and ongoing efforts to maintain healthy populations. Let’s delve into the various conservation efforts that have helped these birds thrive and the challenges they still face.
Historical Decline
In the early 20th century, Canada Geese populations faced significant declines due to overhunting and habitat destruction. Wetlands, crucial for their nesting and feeding, were drained for agricultural and urban development. Additionally, the use of lead shot in hunting led to poisoning, further threatening their numbers.
Legal Protections
The Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918 was a crucial turning point for the conservation of Canada Geese. This act provided legal protection against hunting and harassment, making it illegal to harm or kill these birds without a permit. This legislation laid the foundation for their recovery.
Breeding Programs
Breeding programs have played a significant role in boosting Canada Goose populations. Captive breeding and release programs were established to reintroduce geese into areas where they had disappeared. These programs helped re-establish local populations and promote genetic diversity.
Habitat Restoration

One of the most effective conservation strategies has been the restoration and preservation of wetland habitats. Wetlands serve as critical nesting, feeding, and molting sites for Canada Geese. Conservation organizations and government agencies have worked tirelessly to restore degraded wetlands and protect existing ones from further development.
Urban Adaptation
Interestingly, Canada Geese have shown a remarkable ability to adapt to urban environments. City parks, golf courses, and suburban areas often provide suitable habitats with abundant food and fewer predators. While this adaptation has contributed to their population growth, it has also led to challenges such as human-wildlife conflicts.
Human-Wildlife Conflict Management
As Canada Geese populations have grown, conflicts with humans have increased, particularly in urban and suburban areas. Geese can cause damage to lawns, crops, and public spaces, leading to various management strategies. These include habitat modification, use of deterrents, and controlled hunting in some areas to keep populations at sustainable levels.
Monitoring and Research
Ongoing research and monitoring are essential to understanding the health and dynamics of Canada Goose populations. Scientists track migration patterns, breeding success, and population trends to inform conservation strategies. Satellite tracking and banding programs provide valuable data on their movements and behaviors.
Public Education and Involvement

Educating the public about Canada Geese and their conservation is a vital component of these efforts. Programs aimed at schools, community groups, and the general public help raise awareness about the importance of protecting these birds and their habitats. Citizen science initiatives, such as bird counts and reporting sightings, engage the community in conservation activities.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change poses a new set of challenges for Canada Geese. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect their migratory routes, breeding timing, and habitat availability. Conservationists are working to understand and mitigate these impacts through adaptive management strategies.
International Cooperation
Canada Geese are migratory birds that traverse international borders, requiring cooperation between countries for effective conservation. Agreements and partnerships, such as the North American Waterfowl Management Plan, involve multiple countries working together to protect migratory bird habitats and ensure sustainable populations.
Success Stories and Ongoing Efforts
The resurgence of Canada Goose populations is a conservation success story, demonstrating the effectiveness of protective legislation, habitat restoration, and adaptive management. However, ongoing efforts are necessary to address new challenges and ensure that these birds continue to thrive. Conservationists remain vigilant, adapting strategies to changing environmental conditions and human interactions.
Understanding the conservation efforts for Canada Geese highlights the importance of sustained and collaborative efforts to protect wildlife. Their recovery is a testament to what can be achieved through dedicated conservation actions and community involvement.
Conclusion

As we’ve journeyed through the life of the Canada Goose, we’ve uncovered the many facets that make these birds truly remarkable. From their distinctive appearance and dedicated nesting habits to their varied diet and fascinating behaviors, Canada Geese offer a window into the intricate balance of nature. Their story is one of resilience and adaptability as they navigate both wild and urban landscapes with equal ease.
The conservation efforts that have brought the Canada Goose back from the brink of decline serve as a powerful reminder of the impact humans can have on wildlife. Through legal protections, habitat restoration, and ongoing research, we’ve helped these birds thrive once more. Yet, as we face new challenges like climate change and urbanization, the need for continued vigilance and adaptive strategies remains. Whether you’re an avid birdwatcher, a nature lover, or simply someone who enjoys a walk in the park, taking a moment to observe and appreciate the Canada Goose can enrich your experience. These birds, with their strong family bonds and impressive migratory journeys, remind us of the beauty and complexity of the natural world.








Leave a comment