Introduction
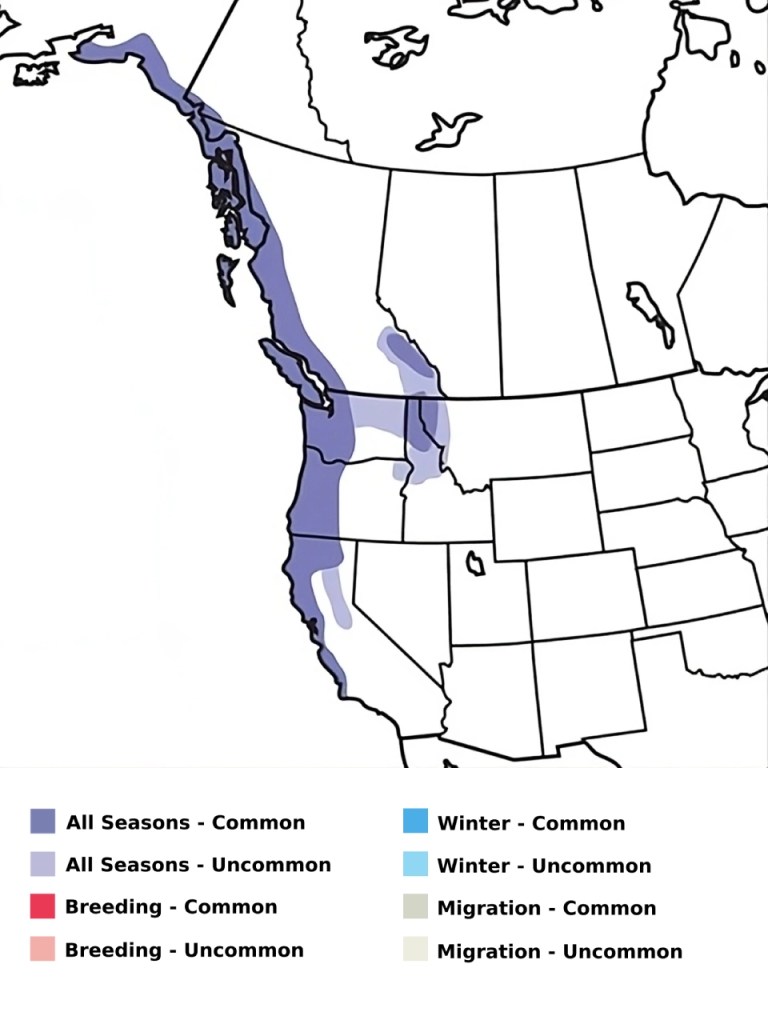
Welcome to the world of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee, a small yet remarkably vibrant bird that captures the hearts of birdwatchers and nature lovers alike. Found primarily along the Pacific Coast of North America, this bird is not only a delight to observe but also plays a crucial role in the ecosystems it inhabits.
In this article, we’ll explore the distinctive features and behaviors of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee. From its unique coloring to its intricate nesting habits and dietary preferences, every aspect of this bird’s life is fascinating. We’ll also delve into some fun facts that make this species stand out from its avian peers and discuss the vital conservation efforts aimed at preserving its habitat and population.
So, whether you’re a seasoned birder or a curious newcomer, prepare to be enchanted by the charismatic Chestnut-backed Chickadee as we dive into its natural world.
Appearance
Let’s start by examining its striking appearance, which not only aids in its survival but also makes it a favorite among photographers and nature enthusiasts. The Chestnut-backed Chickadee is a delight to the eyes, primarily due to its distinctive, multicolored plumage that stands out in its natural habitat.
Size and Shape
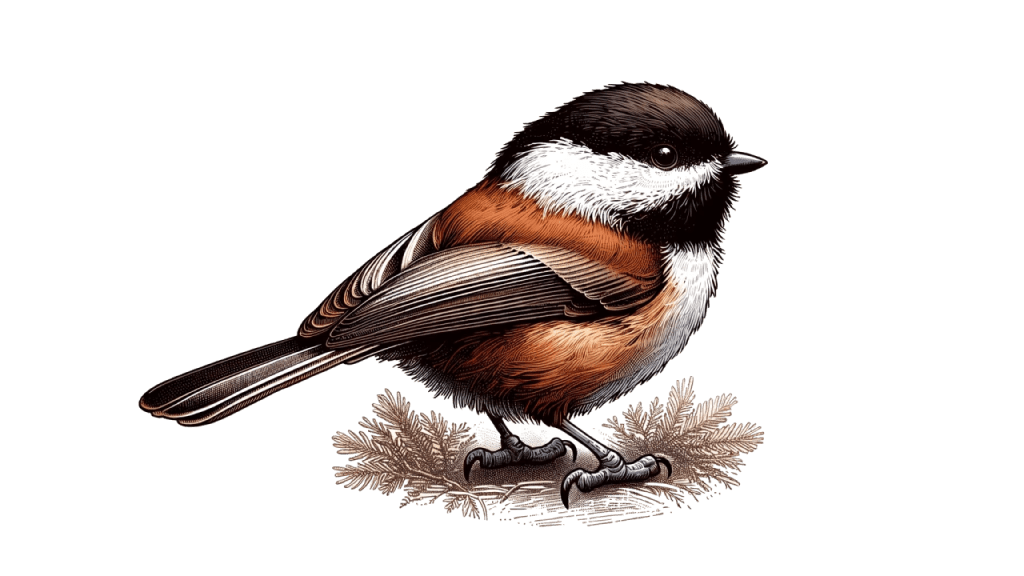
The Chestnut-backed Chickadee is among the smaller birds in the chickadee family. It typically measures about 4 1/2 – 5″ in length and weighs approximately 0.30 – 0.44 oz. Its petite size and round body are complemented by a short neck and large head, creating a charming, fluffy appearance. It sports a short tail and compact wing, which are typical features of the chickadee family that enhance their agility in dense forest environments.
Plumage and Coloration
One of the most prominent features of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee is its color palette. The bird’s striking black cap on its head contrasts sharply with its white cheeks and grayish-white underparts. The name “Chestnut-backed” comes from its beautiful, rich chestnut coloring on the back and flanks, which can vary in intensity depending on the bird’s geographical location and the season.
The juveniles display a more muted version of the adults’ coloring, with softer tones on the back and less contrast in the facial markings. This plumage plays a crucial role in their survival, providing camouflage among the leaves and branches of their habitat.
Molting Patterns
Chestnut-backed Chickadees undergo molting once a year, typically occurring towards the end of summer. During molting, they replace their old feathers with new ones, which are crucial for insulation and waterproofing during the colder months. This annual renewal allows them to maintain the vibrant and insulative qualities of their plumage, which are essential for maintaining body temperature and protection against the elements.
Visual Distinctions Between Sexes

Interestingly, the Chestnut-backed Chickadee exhibits very little sexual dimorphism, meaning that males and females are almost identical in appearance. This lack of distinction can make it challenging to differentiate between the sexes in the wild, relying instead on behavioral cues during mating seasons or other subtle differences.
Adaptations for Habitat
The Chestnut-backed Chickadee’s physical characteristics are not just for show; they are crucial adaptations to its environment. The bird’s small size and agile flight capabilities allow it to maneuver through the dense foliage of its habitat. Its sharp, black eyes are adapted for spotting predators in the low light of its forested habitat, making it an adept survivor in the competitive avian world.
Through its enchanting appearance, the Chestnut-backed Chickadee not only captivates those who observe it but also demonstrates remarkable adaptations that ensure its survival in the wild. This intricate balance of beauty and functionality is just one aspect of what makes studying this bird so rewarding.
Nesting Habits
The nesting habits of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee reflect a fascinating blend of instinct, adaptability, and meticulous care, ensuring the survival of their offspring in their chosen habitats.
Nest Location
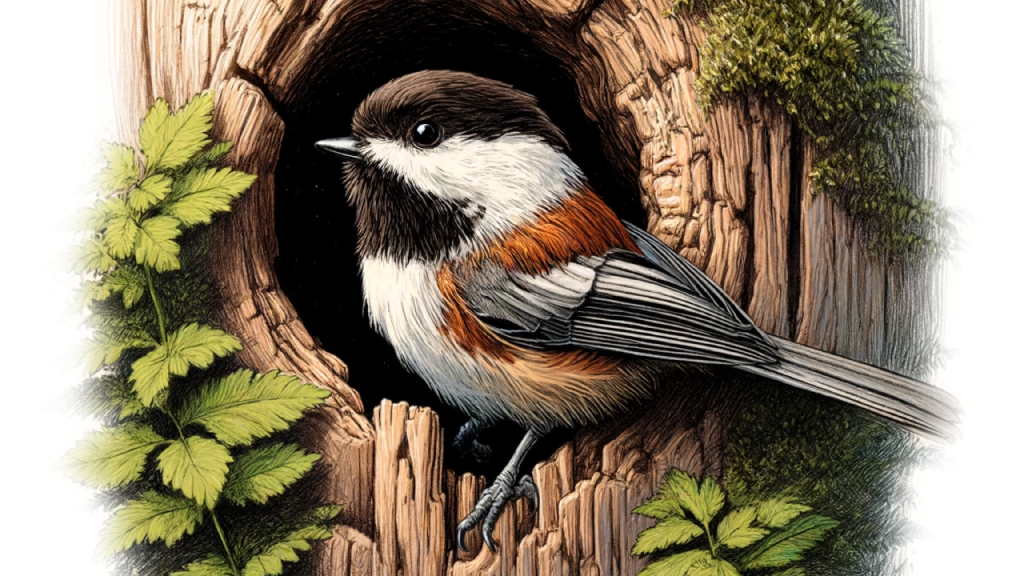

Chestnut-backed Chickadees are cavity nesters, which means they prefer to build their nests in tree hollows. These birds often select sites within dense forests, particularly favoring areas dominated by conifers like Douglas firs and western red cedars. The typical height for their nests can range from just a few feet off the ground to over 20 feet, depending on the availability of suitable nesting sites and the presence of potential threats like predators.
Nest Construction
The construction of a nest by the Chestnut-backed Chickadee is a labor of love and a testament to the bird’s dedication. The female primarily takes on the task, starting with the formation of a base made from moss or bark strips. She then lines the inner cavity with softer materials such as animal fur, feathers, and plant fibers, creating a cozy and insulated environment for her eggs.
Clutch Characteristics
A typical clutch for the Chestnut-backed Chickadee consists of 6 – 7 eggs, which are white with fine specks of reddish-brown. The female incubates the eggs for about two weeks, during which she relies on the male for food and protection.
Parenting and Chick Development
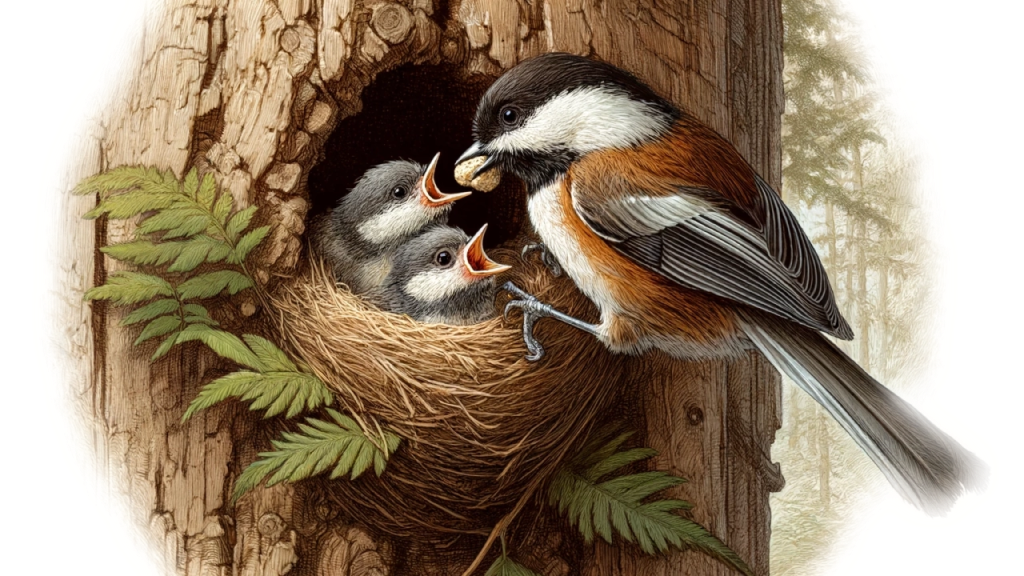

After the chicks hatch, both parents are actively involved in feeding and protecting them. The young chickadees are altricial, meaning they are born vulnerable and without feathers. The development of feathers occurs rapidly, and within three weeks, the chicks are typically ready to leave the nest. This quick growth is essential for their survival, reducing the time they are vulnerable to predators.
Seasonal Timing
The timing of nesting is carefully tuned to the availability of food resources, typically coinciding with the peak abundance of caterpillars and other insects in late spring. This synchronization ensures that there is ample food for the hungry chicks, optimizing their chances of survival.
The nesting habits of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee, from selecting a location to raising chicks, are intricate processes that highlight the bird’s adaptability and the critical role of environmental cues in their reproductive strategies.
Favorite Foods
The Chestnut-backed Chickadee’s diet is an essential aspect of its survival, especially given its small size and the energetic demands of its lifestyle. Let’s take a closer look at the bird’s dietary preferences and how its food choices support its health and reproductive success.
Primary Diet

The Chestnut-backed Chickadee is predominantly insectivorous, relying heavily on a diet of insects and spiders. This diet includes a variety of insect species, such as caterpillars, moths, beetles, leafhoppers, and small wasps, which they glean from the bark and leaves of trees. The high protein content of these insects is crucial for maintaining energy levels, particularly during the breeding season when the demand for nutrients is high.
During the colder months, their diet shifts slightly to include more seeds and berries, providing them with the necessary fats and carbohydrates to endure the winter. They are particularly fond of the seeds from coniferous trees, such as fir and pine, and will also visit bird feeders for suet and sunflower seeds. Attract Chestnut-backed Chickadees to your backyard with this specially designed birdfeeder.
Foraging Behavior
Chestnut-backed Chickadees are active foragers, often seen flitting through the lower and middle levels of trees, searching for food. They employ a methodical approach, examining twigs and leaves meticulously for hidden insects. Their ability to hang upside down on branches allows them to explore various angles, making them incredibly efficient in their search for food.
During the winter, these chickadees often join mixed-species feeding flocks, teaming up with other small birds to increase their chances of finding food and reducing the risk of predation. This social behavior is a testament to their adaptability and strategic thinking when it comes to survival.
Specialized Feeding Adaptations
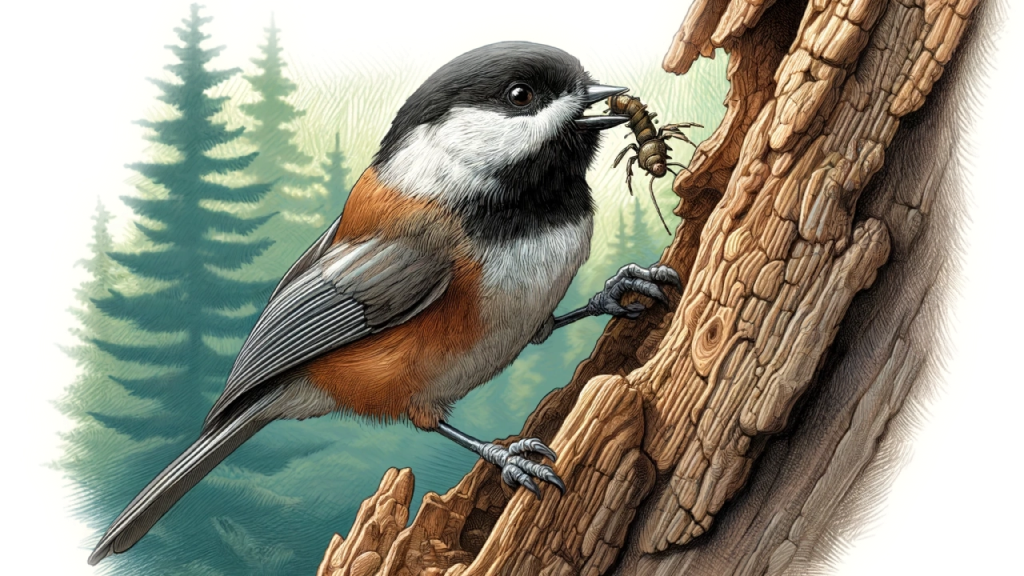

The Chestnut-backed Chickadee’s beak is finely pointed, enabling it to extract insects from tight spaces within the bark. This specialized adaptation is crucial for accessing food sources that are not available to birds with different beak shapes. Additionally, their strong memory helps them relocate caches where they have stored food for later consumption, a vital skill during scarce winter months.
Importance of Diet in Breeding Success
The availability of a protein-rich diet is directly linked to the breeding success of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee. During the spring, when raising chicks, the demand for caterpillars and other soft-bodied insects increases significantly. The parent’s ability to provide a steady supply of these insects is critical for the growth and survival of their offspring.
The Chestnut-backed Chickadee’s dietary habits play a significant role in its ecological niche, influencing everything from its daily energy levels to its reproductive success. By understanding what these birds eat, we gain insights into their behavior, their role in the ecosystem, and the importance of preserving their habitats.
Fun Facts
The Chestnut-backed Chickadee is a fascinating bird due to its appearance and habits. It also has a collection of intriguing characteristics that make it a subject of interest and admiration. Here are some fun facts about this lively little bird that highlight its unique qualities and behaviors.
Vocal Abilities and Communication
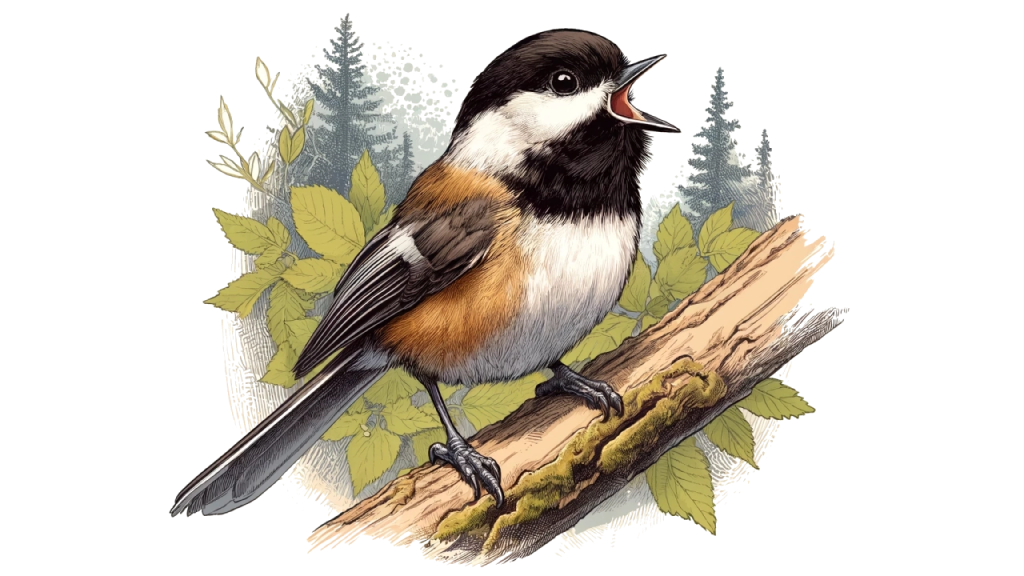

Chestnut-backed Chickadees are known for their complex vocalizations, which include a variety of calls and songs. The Chestnut-backed Chickadee and the Black-capped Chickadee have similar but distinct vocalizations. The Black-capped’s call has the well-known “Chick-a-dee, dee, dee” pattern. However, the call of the chestnut-back is quicker, higher pitched, and buzzier.
Memory Masters
One of the most remarkable traits of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee is its exceptional memory. These birds can remember thousands of locations where they have stored food across their territory. This spatial memory is critical during the winter months when food sources are scarce, and they need to rely on the reserves they cached during more abundant times.
Temperature Regulation
Despite their small size, Chestnut-backed Chickadees are hardy survivors of cold temperatures. They can lower their body temperature during cold nights, entering a state of controlled hypothermia. This adaptation reduces their metabolic rate and conserves energy, enabling them to survive the freezing temperatures of their northern habitats.
Social Structure
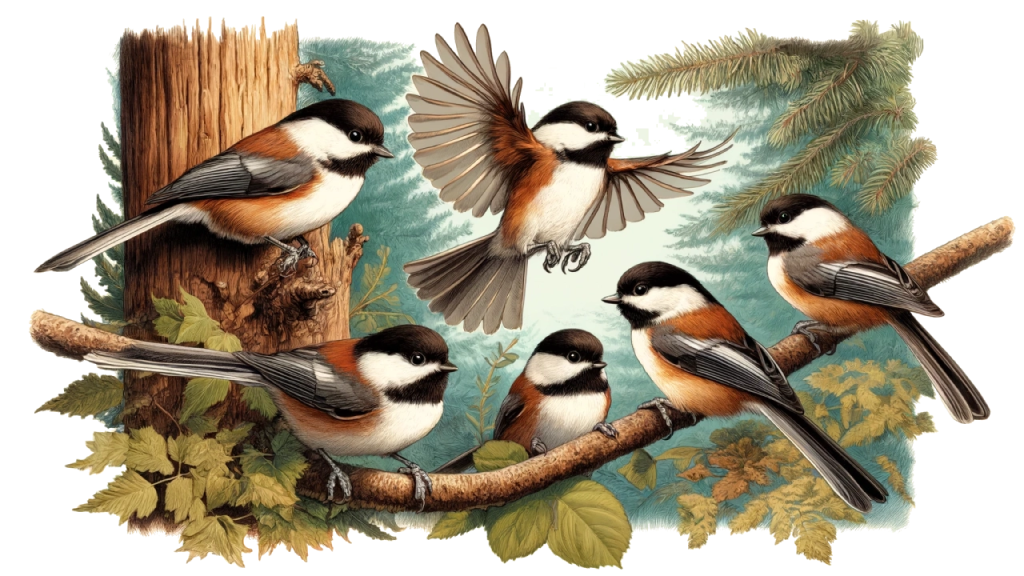

Chestnut-backed Chickadees maintain a complex social structure. Outside of the breeding season, they often form flocks with a clear hierarchy. This social organization helps them defend territories and find food more efficiently. The hierarchy is generally established through subtle displays of dominance and submission, rather than overt aggression.
Lifespan and Survival
In the wild, the average lifespan of a Chestnut-backed Chickadee is about four years, although individuals have been known to live longer under optimal conditions. During banding efforts in California in 2001, the oldest known Chestnut-backed Chickadee was recorded to be 9 1/2 years old. Their survival is heavily influenced by the availability of food and the presence of predators. This species’ adaptability to various environmental conditions underscores its resilience and the effectiveness of its survival strategies.
Conservation Efforts
Like many bird species, the chestnut-backed chickadee faces challenges due to habitat loss, climate change, and other environmental pressures. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of this species, highlighting the importance of both local and broader ecological strategies.
Habitat Protection

One of the primary conservation measures for the Chestnut-backed Chickadee involves protecting and restoring its natural habitat. Since these birds thrive in mature coniferous and mixed forests, efforts to preserve these environments are vital. Conservation organizations and governmental agencies often collaborate to manage forest resources sustainably, ensuring that logging practices do not excessively disturb critical nesting and foraging areas.
Research and Monitoring
Ongoing research is essential to understand the population dynamics and health of Chestnut-backed Chickadees. Banding programs, where birds are safely captured, tagged, and released, help researchers track movements, lifespan, and breeding success. Such data are critical for assessing the impact of environmental changes and conservation policies on the species.
Climate Change Adaptation
As climate change alters the distribution of tree species and the timing of insect availability, adapting conservation strategies to these changes is crucial. Projects that focus on climate resilience, such as forest diversification and creating corridors for wildlife movement, are becoming increasingly important. These initiatives help ensure that the Chestnut-backed Chickadee can find suitable habitats and food sources as environmental conditions evolve.
Community Involvement

Local communities play a significant role in conserving the Chestnut-backed Chickadee. Through educational programs and birdwatching societies, people become more aware of the species and its needs. Community-driven projects, such as planting native trees and creating backyard habitats that include bird feeders and nesting boxes, also contribute to supporting the population.
Advocacy and Legislation
Advocacy for stronger environmental protection laws is another key aspect of conservation efforts. By promoting policies that reduce harmful impacts on forests and wildlife, conservationists aim to secure a safer future for the Chestnut-backed Chickadee. Support for these policies is often bolstered by the bird’s popularity among the public and its role as an indicator species for the health of forest ecosystems.
Through these multifaceted conservation efforts, there is hope for maintaining the population and health of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee. Protecting this species benefits the chickadees and enhances the biodiversity and stability of their ecosystems.
Conclusion
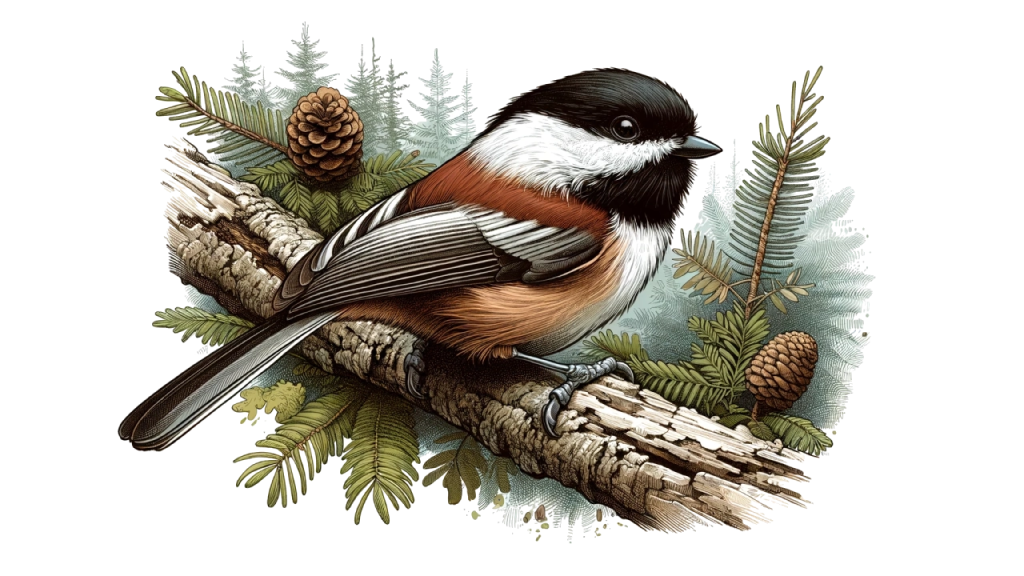

The charming Chestnut-backed Chickadee is much more than just a pretty face. With its complex behaviors, remarkable adaptability, and engaging presence, the Chestnut-backed Chickadee offers endless fascination for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts alike. From its striking appearance to its intriguing vocalizations and resilient survival strategies, every aspect of this bird exemplifies the wonder of the natural world.
Conservation efforts play a critical role in ensuring that future generations will continue to enjoy the presence of the Chestnut-backed Chickadee. Protecting its habitat, engaging communities in conservation, and adapting strategies in response to environmental changes are all crucial for the bird’s survival. Each of us can contribute to these efforts, whether by supporting local conservation initiatives, participating in citizen science projects, or simply spreading awareness about the importance of biodiversity. The Chestnut-backed Chickadee reminds us of the interconnectedness of our ecosystems and the importance of each species within it. By valuing and protecting these birds, we not only preserve their beauty and ecological roles but also maintain the health of our environment for all its inhabitants.








Leave a comment